Calc.exe is a .NET program (finally :D), which can evaluate (mostly) mathematical expressions.
At first no functions are enabled except some basic mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, etc.
But we can enable different functions by using a digitally signed X509 certficates.
We also got an example cert “guestCert.crt” which enabled some basic math and trigonomical functions.
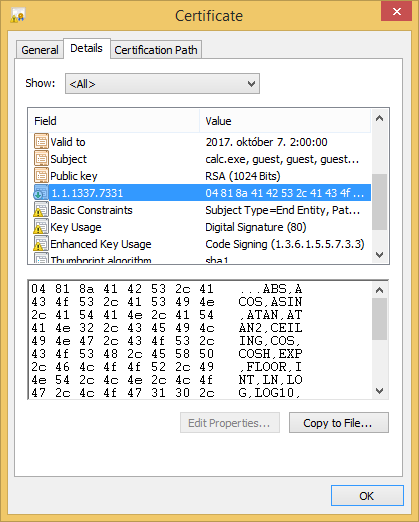
The program also adds a function called FLAG which returns the flag as string.
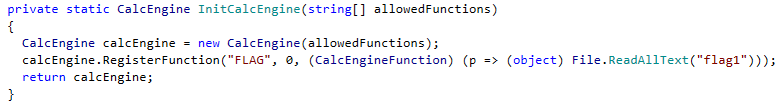
The problem is we cannot load any certificate as there is a lot of checks before, so we had to find some vulnerability. The program uses a known crypto library, called BouncyCastle and the attached “BouncyCastle.Crypto.dll” is exactly the same as the one we can download from NuGet. As no known vulnerability exists for this library (or at least at the certificate verification part), we had to look for vulnerabilities in the program.
Although the certificate loaded into the store while it is checked, no self-signed certificates are allowed and it is removed as soon as its verification fails.
But there is a bug in the code: although some checks like the VerifyCertificate is in a try-catch block and returns a boolean value, the IsCalcExeCert can throw exception while calling SingleOrDefault method. To trigger the exception we have to put two values with the 2.5.4.1337 key into the SubjectName’s field.
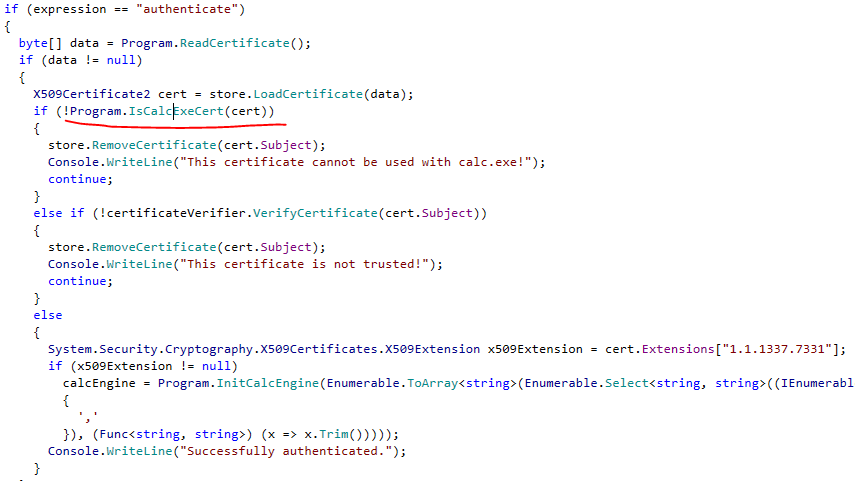
Although our certificate is not deleted from the trusted CA store, it is not loaded into the program, so we cannot call the FLAG function yet. But we can sign a new client certificate with this now trusted cert as a CA (certificate authority). This way our new certificate will be accepted.
The attached C# code snippet (calcexe1.cs) will generate the fake CA and the fake certificate.
The flag was: ASIS{e5cb5e25f77c1da6626fb78a48a678f3}Exploit code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.ConstrainedExecution;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Asn1;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Asn1.X509;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Crypto;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Crypto.Generators;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Crypto.Parameters;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Crypto.Prng;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Math;
using Org.BouncyCastle.OpenSsl;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Pkcs;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Security;
using Org.BouncyCastle.Utilities;
using Org.BouncyCastle.X509;
namespace CalcExeCertGenerator
{
class Program
{
public class CertWithKey
{
public X509Certificate Cert { get; set; }
public RsaPrivateCrtKeyParameters Key { get; set; }
public CertWithKey(X509Certificate cert, RsaPrivateCrtKeyParameters key)
{
Cert = cert;
Key = key;
}
}
public static CertWithKey GenerateCertificate(string subjectName, CertWithKey issuer = null, int keyStrength = 1024, Action<X509V3CertificateGenerator> genAction = null)
{
var random = new SecureRandom(new CryptoApiRandomGenerator());
var certificateGenerator = new X509V3CertificateGenerator();
certificateGenerator.SetSerialNumber(BigIntegers.CreateRandomInRange(BigInteger.One, BigInteger.ValueOf(Int64.MaxValue), random));
certificateGenerator.SetSignatureAlgorithm("SHA1WithRSA");
certificateGenerator.SetIssuerDN(issuer != null ? issuer.Cert.SubjectDN : new X509Name(subjectName));
certificateGenerator.SetSubjectDN(new X509Name(subjectName));
certificateGenerator.SetNotBefore(DateTime.UtcNow.Date);
certificateGenerator.SetNotAfter(DateTime.UtcNow.Date.AddYears(2));
certificateGenerator.AddExtension(X509Extensions.BasicConstraints, true, new BasicConstraints(false));
certificateGenerator.AddExtension(X509Extensions.KeyUsage, true, new KeyUsage(KeyUsage.DigitalSignature));
certificateGenerator.AddExtension(X509Extensions.ExtendedKeyUsage, true, new ExtendedKeyUsage(KeyPurposeID.IdKPCodeSigning));
if (genAction != null)
genAction(certificateGenerator);
// Subject Public Key
var keyPairGenerator = new RsaKeyPairGenerator();
keyPairGenerator.Init(new KeyGenerationParameters(random, keyStrength));
var subjectKeyPair = keyPairGenerator.GenerateKeyPair();
certificateGenerator.SetPublicKey(subjectKeyPair.Public);
var certificate = certificateGenerator.Generate(issuer != null ? issuer.Key : subjectKeyPair.Private, random);
return new CertWithKey(certificate, (RsaPrivateCrtKeyParameters)subjectKeyPair.Private);
}
static string ToPem(object obj)
{
var sw = new StringWriter();
new PemWriter(sw).WriteObject(obj);
return sw.ToString();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
X509Name.DefaultLookup.Add("prg", new DerObjectIdentifier("2.5.4.1337"));
var fakeCa = GenerateCertificate("C=IR, L=Iran, [email protected], O=calc.exe, CN=calc.exe, 2.5.4.1337=calc.exe, 2.5.4.1337=calc.exe");
var fakeUserCert = GenerateCertificate("C=IR, L=Iran, [email protected], O=guest, CN=guest, 2.5.4.1337=calc.exe", fakeCa,
genAction: gen => gen.AddExtension("1.1.1337.7331", false, Encoding.Default.GetBytes("ABS,ACOS,ASIN,ATAN,ATAN2,CEILING,COS,COSH,EXP,FLOOR,FLAG,INT,LN,LOG,LOG10,PI,POWER,RAND,RANDBETWEEN,SIGN,SIN,SINH,SQRT,SUM,SUMIF,TAN,TANH,TRUNC,READ,WRITE")));
File.WriteAllText("fakeCa.crt", ToPem(fakeCa.Cert));
File.WriteAllText("fakeUserCert.crt", ToPem(fakeUserCert.Cert));
}
}
}