This challenge was solved by and the write up was written by one of my teammates, NGG.
The task was to break a TLS connection where DHE was used but not with a safe prime.
I extracted the group parameters and the public keys from Wireshark.
To get the private keys I had to compute the discrete logarithm of the public keys, Sage has a builtin function discrete_log() for this.
That function internally uses the Pohlig-Hellman algorithm, the problem’s name was a reference to this.
After I had the private keys, I computed the shared secret (= server private key ** client public key = client private key ** server public key).
TLS uses this shared secret as the Pre-Master Secret.
Recent Wireshark versions support PMS_CLIENT_RANDOM lines in SSL key log files, which means that I could give it the Client Random and the PMS.
Unfortunately this didn’t work, Wireshark didn’t properly parsed that line.
I fixed this issue in Wireshark, and later submitted the fix for them, it has been merged into the main Wireshark repo: https://github.com/wireshark/wireshark/commit/a386fc99ac72b4cdb88cb3d26fd19d6251391b96
After this patch it successfully decrypted the TLS session and I got the flag.
KT’s notes
Wireshark did not recognised the SSL stream for me by default, so I had to use the Decode As… > SSL option to make this work.
While NGG patched the Wireshark, I used Bouncy Castle to generate the master secret from the pre-master secret as Wireshark could decode the packet by using the master secret (but NOT with the pre master secret).
But I had to use the new PRF function which is used by TLS v1.2, the SHA256 one. I first tried to use the legacy (MD5+SHA1) one which did not work of course.
The decrypted stream was gziped too, so I had to decompress it manually.
Here is my python code to calculate the pre master secret from the private key primes (provided by NGG):
g = 15
p = 120154561482812169366431552175315487829790853533514455083187141150401404579723989466386713554692826031183462112641793395815695957964420754471645865010199918851008631038679685035857813488382170765657628252079464574576993595350214255290554756868269962991079417299897885957935578968328491235168443836989742332343
serverPub = 15369826910045798505944602235292509575421896014593476253460520436999422262976808201559207167484626647165429162578239702208851445339474080566111254064294894686179067829420678898877680468207865053420154070753622998449913849113660665890563557345041388819744669458524582116729348785032868594899974751301992211942
clientPriv = 60718865604238636792448303494365716882164666056259649436621448321833526997406139737129717809752411282395923980538280108384420161312200897847011832376271391686584918997410839768394294177900987398210617282873117230335140878980614031856353751625633843722321910793427876767949814642081894104118067451970498867957
serverPriv = 59006032085539066654738961800014267746790599707391816715596169525214790059448996782118611368019640695755528975737064604557552323199458051510791227341575474224365096322734016366705156141900274852582650051394166907890512962805910611488014074434283648737771547999795442960002220587672342309646529188635103348462
clientPub = 105015090494516026290331080495860554512811478600077917407214638372179160992689979146469996516559216693457065339039865100354916844456254305946233030576312061960323729497136060115320306445494733252851807759941954458152508254981769624193022726156751468585330721382626827982843354097562826035890756697793638835353
assert(serverPub == pow(g, serverPriv, p))
assert(clientPub == pow(g, clientPriv, p))
preMasterSecret = pow(serverPub, clientPriv, p)
hex(preMasterSecret)And this is my C# code to calculate the master secret from the premaster secret:
var premaster = new BigInteger("97767226768431843909574565470123616032917083203013628903095612670005753675445500525763667655689728731939280038960341016957753437419456873567523867888108036157325629926777593214675498958231293240650034816836615958992638881953048254604005620980597958229509174130519560051229345937360583880913807554453333987854");
var masterSecret = TlsUtilities.PRFHack(premaster, "master secret", TlsUtilities.Concat(
HexToBytes("7712ca85fcd84204104909836b7c92cec6094277f1c0efe885102d74a30b6dcc"),
HexToBytes("63e2b53d65a8e860794ff15e90e7a369b179843f349b68df4b59d1ac53003735")), 48);
var masterSecretHex = BitConverter.ToString(masterSecret).Replace("-", "").ToLower();Setting this file in File > Preferences > Protocols > SSL as the (Pre)-Master-Secret log filename I could follow the SSL with the unpatched Wireshark too:
CLIENT_RANDOM 7712ca85fcd84204104909836b7c92cec6094277f1c0efe885102d74a30b6dcc 599dae45bea108da405cebfa1fd4414acccdc24ab4262c1c1e86af60da2de9712933343d3c6f92486db4bdbda9d693f8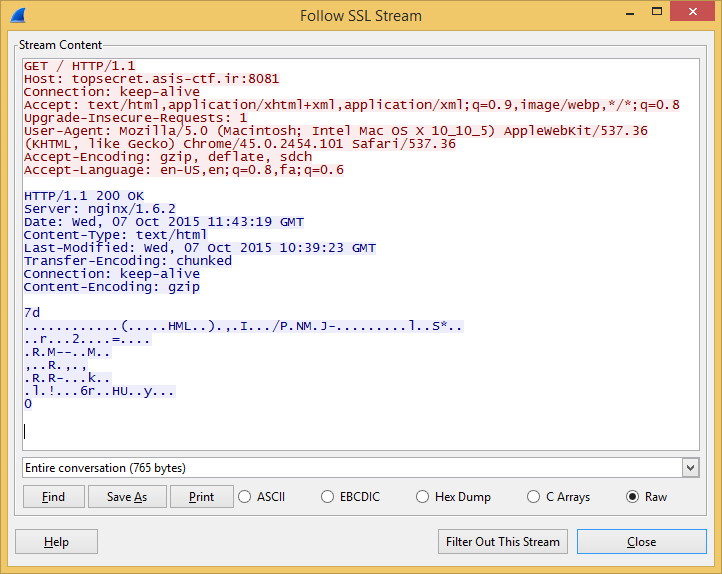
After decompressing the HTTP response body I got the file’s content:
Flag is ASIS{f702d759801533096be29291fd6e82c3}